A Strategic Guide for Business Leaders: 6 Science-Backed Office Layouts to Boost Productivity by 40%

In the world of business, one fact remains constant: the environment in which we work directly impacts how well we work. This connection between workspace design and productivity is not just anecdotal; it's rooted in the science of neuroscience and environmental psychology. As decision-makers, it’s crucial to recognize that the layout of your office influences both the cognitive processes and overall well-being of your team.
Space layout affects cognitive performance through three distinct neural mechanisms. These mechanisms are driven by how our brain interacts with the space around us, influencing our attention, focus, and stress levels. Specifically, the brain responds to environmental factors such as noise, light, and spatial organization, which can either foster or hinder productivity.
When designing an office, it’s not just about creating a pleasant aesthetic; it’s about engineering an environment that optimizes brain function. With remote work on the rise and Zoom fatigue becoming increasingly common, modern offices must be designed to accommodate different working styles and activities—an environment where cognitive resources are maximized and distractions minimized.

Modern Office Pain Points: The Struggles of Today's Workspace
Many businesses are dealing with the challenge of creating office environments that foster both collaboration and deep focus. The traditional open-plan office—once hailed as the ideal workspace for creativity—has now become a breeding ground for distractions, noise, and a lack of privacy. Meanwhile, employees working remotely are left feeling isolated and disconnected.
This brings us to a key issue: how can organizations balance the need for collaboration with the desire for privacy and concentration? The answer lies in understanding the spatial dynamics that influence work efficiency.
In the workplace, productivity is influenced by three core factors:
Focus: The ability to work without interruption.
Collaboration: The ability to engage in team discussions and brainstorming.
Distraction: External factors that hinder concentration, such as noise, visual clutter, or inappropriate lighting.

To address this, we propose the "Space Productivity Formula":
E = (F × C) / D²
Where:
E is productivity.
F is focus (how well employees can concentrate).
C is collaboration (how easily employees can interact with others).
D² is the square of distraction (how much external disruption occurs in the workspace).
The goal is to create environments where focus and collaboration are maximized while minimizing distractions, which can be achieved through scientifically-backed office layouts.
Core Layout Systems: 6 Scientific Models
1. The Cognitive Restoration Layout (Attention Restoration Theory)
Cognitive Science Principle:
Attention Restoration Theory (ART) suggests that our brains need moments of rest from high-focus tasks. Natural environments, or spaces that mimic nature, allow for cognitive restoration by providing a calming effect on the brain, reducing mental fatigue.
Space Parameters:
Space per person: 150-200 sq ft.
Partition height: 4-5 ft to maintain openness while providing privacy.
Walking flow: Design pathways that lead to quiet areas with minimal distractions.
Environmental Control Metrics:
Temperature: 68°F - 72°F for optimal comfort.
Noise threshold: Background noise levels between 35-45 dB to maintain a peaceful atmosphere.
Lighting gradient: Use natural daylight where possible, with adjustable light intensity (300-500 lux).
Transition Mechanism:
Focus Mode: Use plants, soft lighting, and soundproofing materials in quiet zones for deep work.
Collaboration Mode: Create nearby open spaces with ergonomic seating for informal meetings and group activities.

2. The Open Collaboration Hub (Social Facilitation)
Cognitive Science Principle:
Social Facilitation Theory suggests that the presence of others can enhance performance in group tasks. This layout design maximizes the benefits of social interactions for collaborative tasks and brainstorming sessions.
Space Parameters:
Space per person: 100-120 sq ft.
Partition height: 3 ft for visibility and easy interaction.
Walking flow: Create an open space where teams can easily move and gather.
Environmental Control Metrics:
Temperature: 72°F - 75°F for comfort during group activities.
Noise threshold: Higher noise levels of 45-55 dB to encourage social interaction and creativity.
Lighting gradient: Bright lighting (500-800 lux) to energize the team during brainstorming or creative work.
Transition Mechanism:
Collaboration Mode: Set up group tables and communal workspaces with comfortable seating arrangements to encourage interaction.
Focus Mode: Establish quiet zones with acoustic barriers and soft lighting for tasks that require deep concentration.
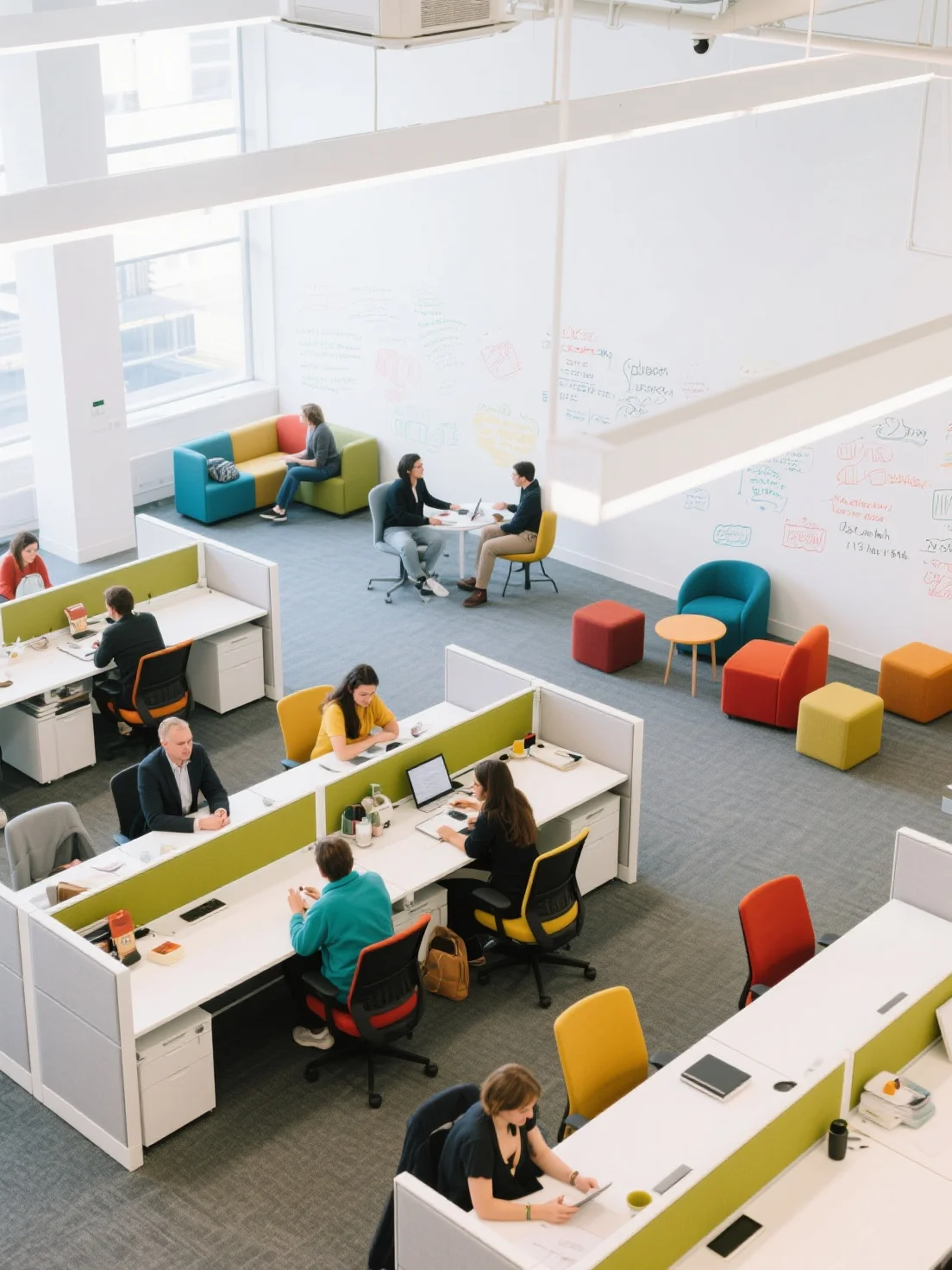

3. The Hybrid Workspace (Flow State Optimization)
Cognitive Science Principle:
Flow State Theory suggests that employees are most productive when they are in a state of "flow"—a mental state where they are fully immersed and engaged in their work. The hybrid workspace design supports switching between tasks and maximizing flow states by providing flexibility and ease of movement.
Space Parameters:
Space per person: 120-150 sq ft.
Partition height: Modular, adjustable partitions to create personalized space.
Walking flow: Easy transition between collaborative and private areas.
Environmental Control Metrics:
Temperature: 70°F - 72°F for consistent comfort.
Noise threshold: Variable, with quiet zones (30-40 dB) and active areas (50-60 dB).
Lighting gradient: Adjustable lighting (400-600 lux) to cater to different work modes.
Transition Mechanism:
Focus Mode: Utilize soft seating, adjustable partitions, and acoustic panels to allow employees to work deeply.
Collaboration Mode: Flexible meeting areas with mobile seating and technology to facilitate team collaboration.
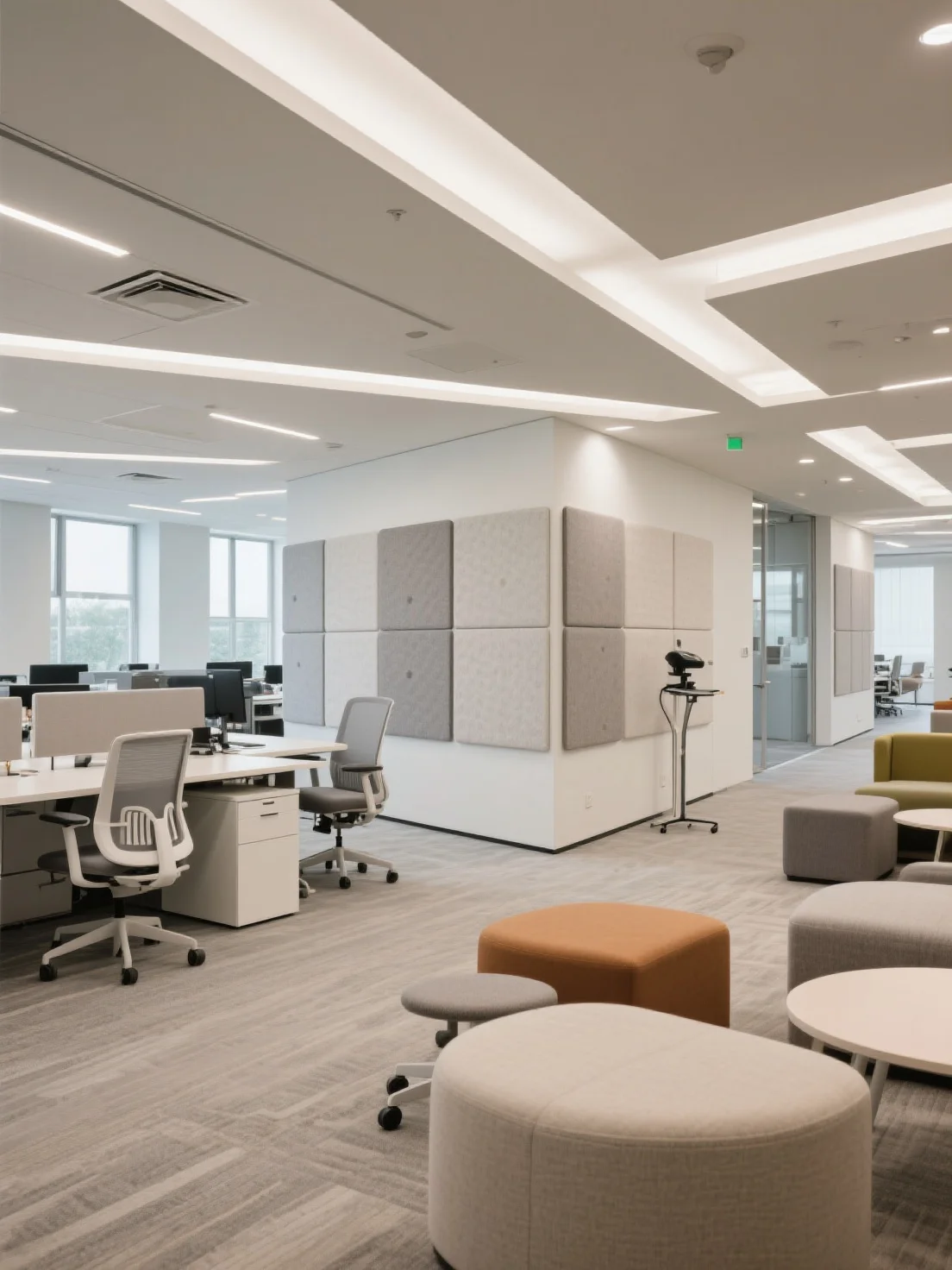

4. The Privacy-First Space (Stress Reduction and Cognitive Load Theory)
Cognitive Science Principle:
Cognitive Load Theory explains that multitasking and distractions increase cognitive strain, reducing efficiency. Privacy-first spaces help reduce this strain by providing employees with quiet, undisturbed environments for focused work.
Space Parameters:
Space per person: 120-160 sq ft.
Partition height: 5-6 ft partitions to create privacy while allowing interaction.
Walking flow: Ensure designated quiet zones for deep work with minimal foot traffic.
Environmental Control Metrics:
Temperature: 68°F for optimal focus.
Noise threshold: Very low, <30 dB to minimize distractions.
Lighting gradient: Low to moderate lighting (250-400 lux) in quiet zones to promote relaxation.
Transition Mechanism:
Focus Mode: Designate soundproof, enclosed rooms with ergonomic furniture to help employees focus without interruptions.
Collaboration Mode: Separate collaborative spaces with whiteboards and brainstorming materials for creative work.
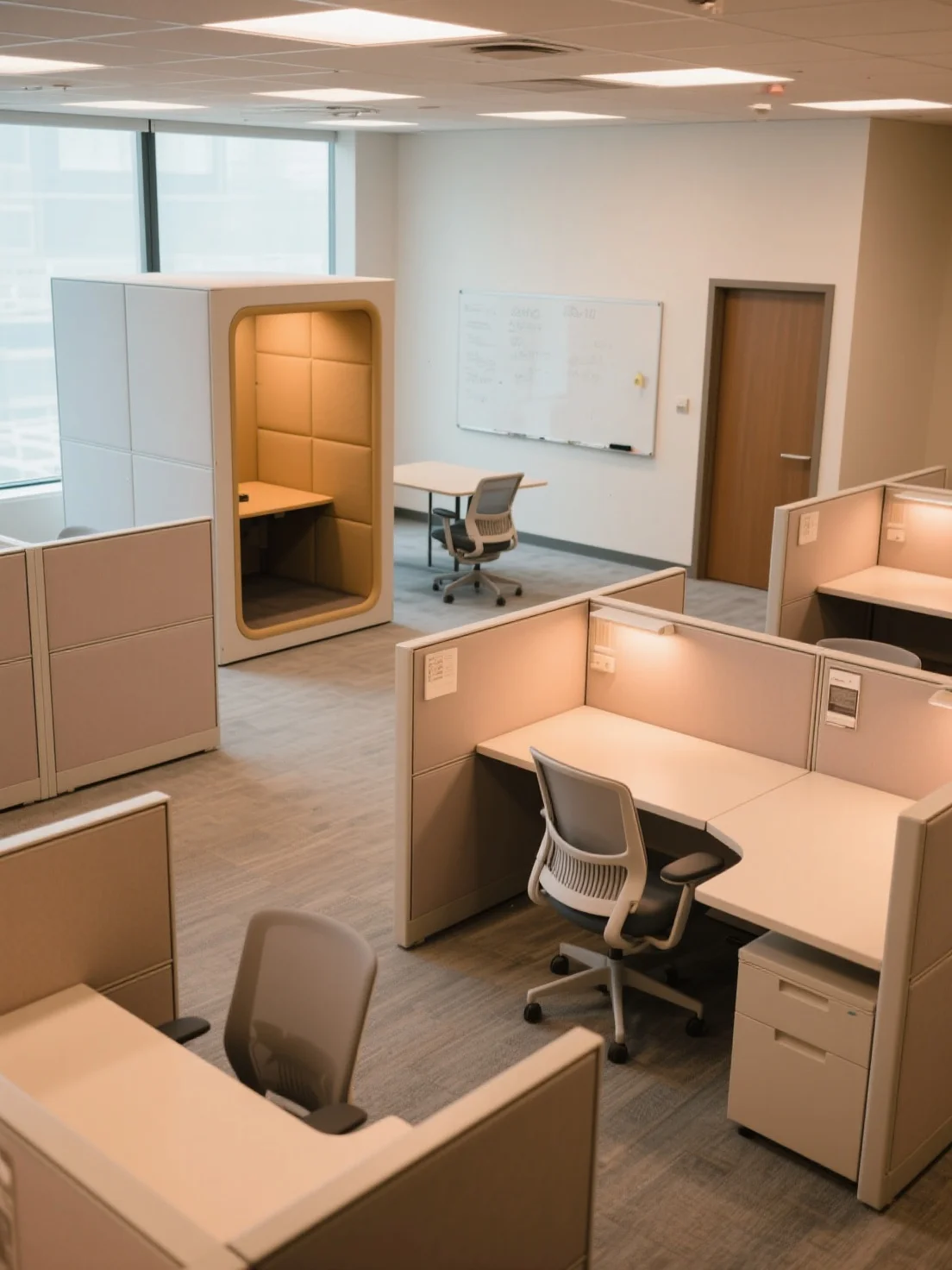

5. The Activity-Based Layout (Task Complexity Theory)
Cognitive Science Principle:
Task Complexity Theory suggests that tasks of different complexity levels require different types of environments. An activity-based layout allows employees to choose the optimal space based on the task they are working on.
Space Parameters:
Space per person: 100-150 sq ft, depending on task.
Partition height: Flexible, with movable walls to create open or closed workspaces.
Walking flow: Multiple workstations allowing for easy movement between areas with different setups.
Environmental Control Metrics:
Temperature: 70°F - 74°F to accommodate a range of work styles.
Noise threshold: Varies between 40-50 dB for individual tasks and 55-65 dB for group activities.
Lighting gradient: Adjustable lighting settings to accommodate different work tasks (300-800 lux).
Transition Mechanism:
Focus Mode: Areas designed with minimal distractions and soft acoustics for deep, individual work.
Collaboration Mode: Large, open spaces with flexible seating and collaboration tools to facilitate group discussions.
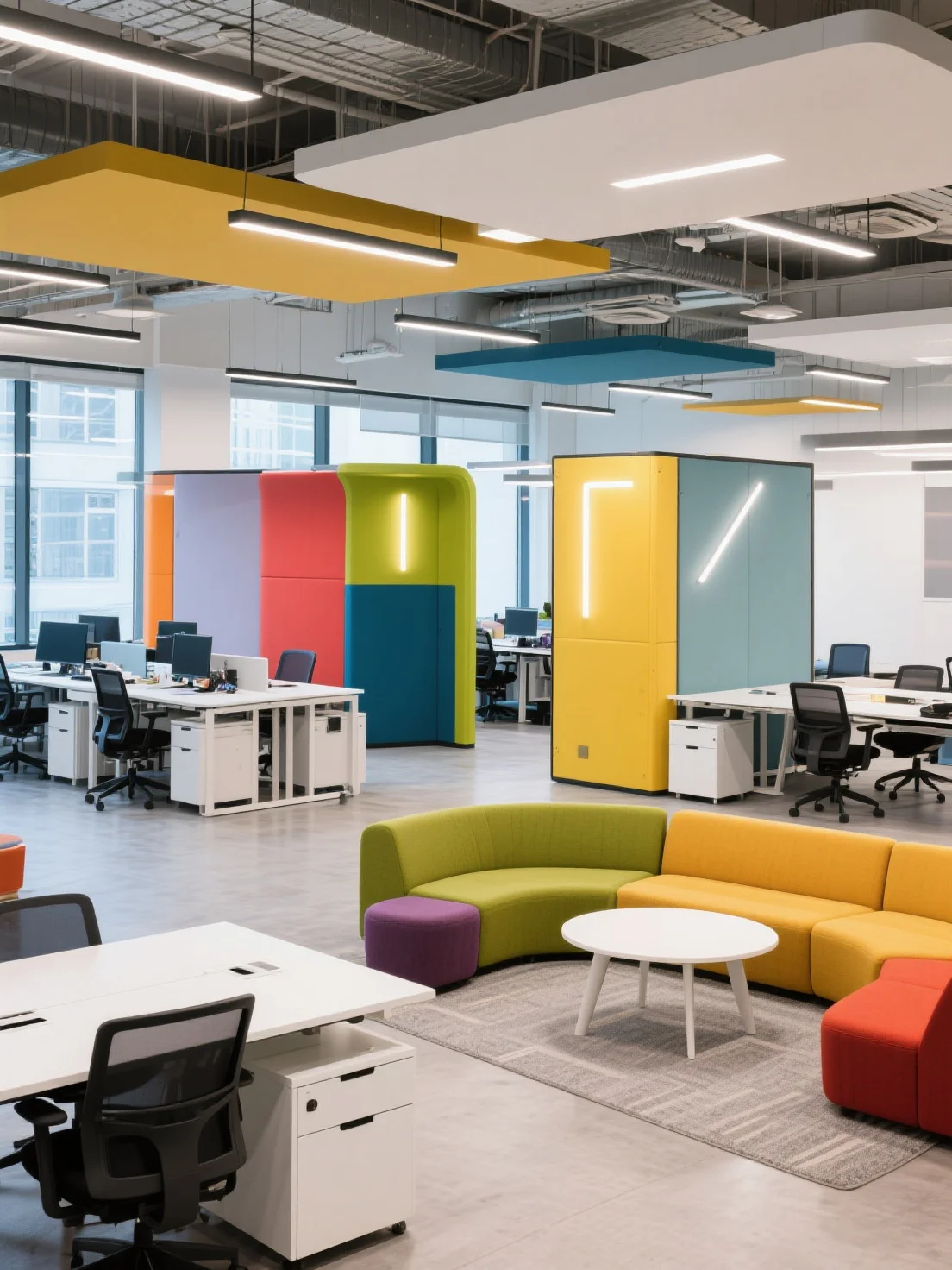

6. The Ergonomic Office (Human Factors Engineering)
Cognitive Science Principle:
Human Factors Engineering focuses on optimizing the physical environment to reduce stress and physical strain, improving cognitive performance. An ergonomic office layout promotes productivity by supporting healthy work habits and minimizing physical discomfort.
Space Parameters:
Space per person: 100-140 sq ft.
Partition height: No partitions, or low modular walls.
Walking flow: Pathways should be clear, with well-placed furniture for movement.
Environmental Control Metrics:
Temperature: 70°F - 73°F for comfort.
Noise threshold: Moderate (40-50 dB) to encourage focus without distractions.
Lighting gradient: Bright task lighting (500-600 lux) to prevent eye strain.
Transition Mechanism:
Focus Mode: Ergonomically designed individual desks with adjustable chairs to ensure comfort and reduce physical strain.
Collaboration Mode: Collaborative spaces with height-adjustable tables and comfortable seating.

How to Evaluate Your Office: Using Efficiency Heat Map Analysis to Boost Productivity
As businesses continue to adapt to the evolving workplace needs, it’s crucial to assess whether your office layout is truly optimized for productivity. To achieve this, we recommend using the Efficiency Heat Map Analysis, a method grounded in cognitive science and office design principles. This approach enables you to visualize how effectively your office layout supports work efficiency, focus, and collaboration.
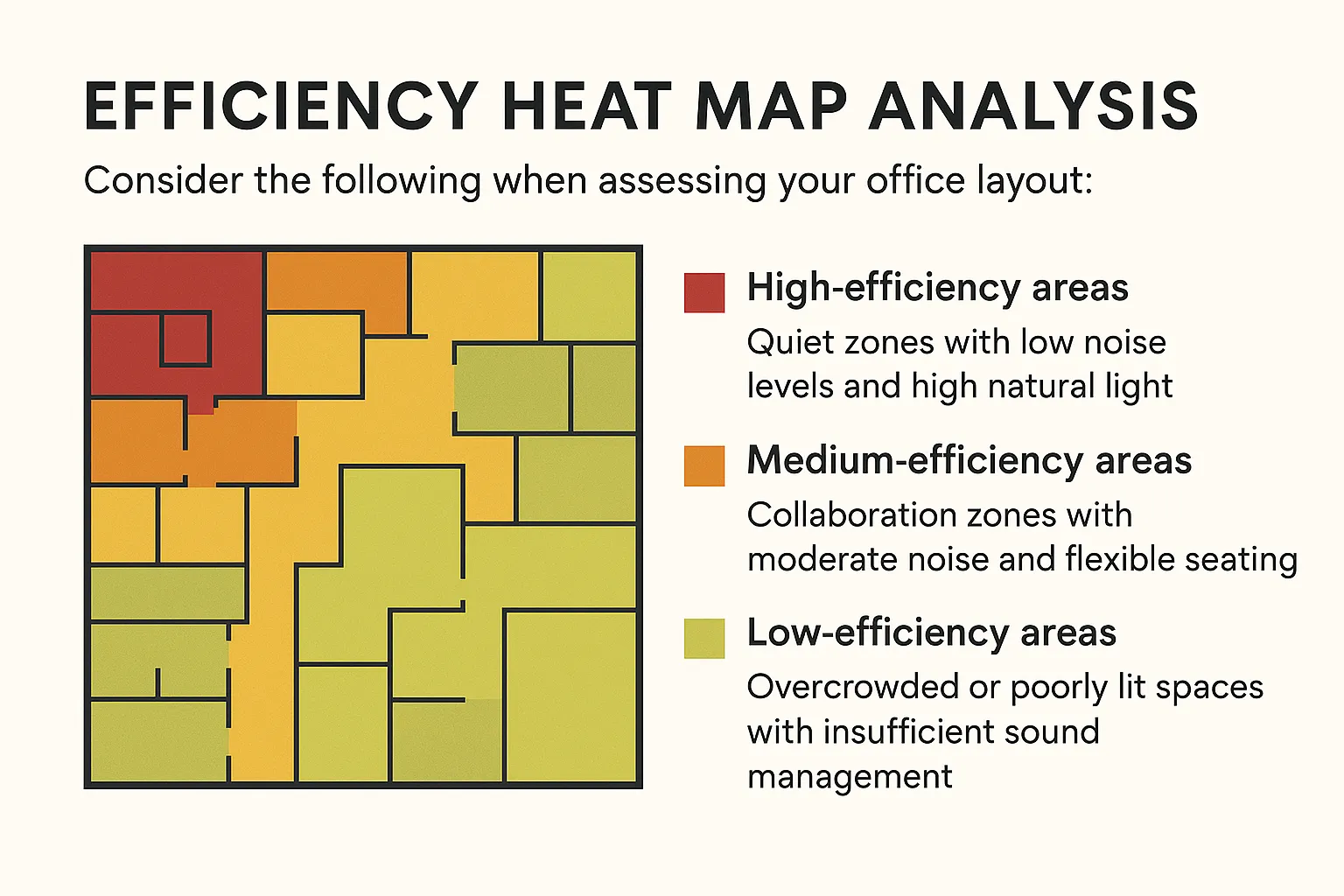
How to Use the Heat Map in Your Office Design
Once the Efficiency Heat Map has been created, it’s time to apply the findings to your office layout:
Rearrange Furniture: Move furniture to create clear zones for focus and collaboration.
Optimize Quiet Zones: Enhance privacy and reduce noise by adding partitions, acoustic panels, or even plants to absorb sound.
Encourage Collaboration: For medium-efficiency areas, consider incorporating versatile, mobile furniture and ensuring ample space for team meetings.
Improve Lighting: Add more light sources to dark areas, and consider installing adjustable lighting to cater to various tasks.
Address Temperature and Ventilation: Ensure consistent, comfortable temperature levels across the office by adding fans or adjusting HVAC systems.
By applying the science-backed principles behind these 6 office layout models, businesses can create environments that foster productivity, collaboration, and focus. These strategies are not only about aesthetics but also about enhancing cognitive function, reducing stress, and optimizing space use. At Artivano, we believe in the power of intelligent design—creating spaces that not only look great but also enhance the well-being and productivity of the people who inhabit them.







